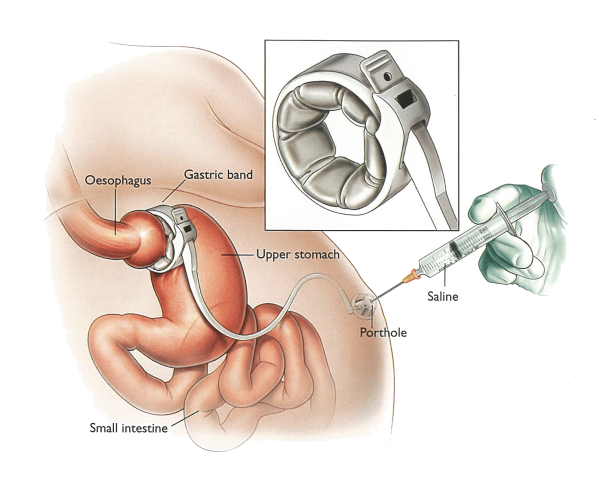
Gastric band adjustment represents a critical component in the long-term success of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) procedures. This minimally invasive surgical technique involves placing a silicone band around the upper portion of the stomach, creating a small pouch that restricts food intake and induces earlier satiety. Research demonstrates that proper band adjustment protocols significantly impact weight loss outcomes, with patients receiving systematic adjustments losing an average of 47% of excess body weight compared to 38% in those with less structured follow-up. The adjustment process involves adding or removing saline solution through a subcutaneous port, allowing physicians to customize restriction levels based on individual patient needs and responses.
Table of Contents
The timing and frequency of gastric band adjustments follow evidence-based patterns established through clinical practice. Initial adjustments typically occur 4-6 weeks post-surgery once surgical edema has resolved, followed by regular adjustments every 4-8 weeks during the first year. During these sessions, clinicians evaluate weight loss progress, food tolerance, and potential complications such as dysphagia or reflux. Patient-reported symptoms guide adjustment decisions, with clinical indicators including the ability to consume solid foods comfortably, portion size tolerance, and hunger patterns between meals. Medical centers implementing comprehensive adjustment protocols report significantly lower complication rates (9.8% versus 18.2%) and higher patient satisfaction scores compared to facilities without standardized approaches.
Gastric Band Surgery and Adjustment Methods
Adjustable gastric banding represents a minimally invasive bariatric procedure that involves placing an adjustable silicone device around the upper portion of the stomach. The functionality of the lap band tightening mechanism relies on precision engineering that allows healthcare providers to modify restriction levels according to patient needs.
- Adjustable band components:
- Silicone band with inflatable inner balloon
- Access port placed beneath the skin of the abdomen
- Connecting tubing system
- Locking mechanism to maintain band position
The private gastric band adjustment occurs through a straightforward yet highly specialized medical procedure. Practitioners utilize specific equipment to access and modify the band’s tightness without requiring additional surgery after the initial placement.
- Equipment used for adjustments:
- Huber needle (non-coring needle)
- Fluoroscopic guidance systems
- Sterile saline solution
- Pressure monitoring devices
- Band adjustment measurement tools
The gastric band adjustment procedure involves adding or removing saline solution through the access port. Medical professionals perform this procedure in clinical settings, typically as an outpatient service requiring approximately 15-30 minutes to complete.
- Port location and preparation:
- The physician locates the access port using manual palpation or fluoroscopy
- The area is cleaned with antiseptic solution
- Local anesthetic may be administered for patient comfort
- Fluid adjustment process:
- A Huber needle is inserted through the skin into the access port
- Current band fill volume is assessed
- Saline is added or removed according to clinical assessment
- The needle is withdrawn and a small bandage is applied
The technology behind the adjustable stomach band has evolved significantly since its introduction. Modern bands feature improved materials with greater durability and refined design elements that enhance both safety and efficacy profiles.
Innovations in adjustable band surgery techniques include port placement optimization and improved band geometry. These advancements have contributed to more predictable adjustment outcomes and reduced complication rates in clinical practice.
The precision of adjustment of gastric band systems varies between manufacturers, with some devices offering increments as small as 0.1ml of fluid. This level of precision allows for highly personalized restriction management tailored to individual metabolic requirements and weight loss goals. The precision of adjustment also influences the Gastric Band Surgery Price, as more advanced systems with smaller increments can be costlier. Nonetheless, the investment in such precise equipment ensures better long-term outcomes for patients.
Timing and Frequency of Gastric Band Adjustments
The optimal adjustment schedule for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) varies significantly based on individual patient factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for achieving maximum weight loss results and maintaining long-term restriction effectiveness.
Key factors influencing adjustment timing:
- Initial weight and BMI – Patients with higher starting weights typically require earlier and more frequent adjustments
- Rate of weight loss – Slower than expected weight reduction often indicates adjustment necessity
- Individual anatomy – Esophageal and stomach tissue characteristics affect band responsiveness
- Medical history – Previous abdominal surgeries may influence adjustment protocols
- Metabolic profile – Conditions like diabetes can alter optimal adjustment schedules
The development of personalized adjustment protocols follows a systematic approach:
- Baseline assessment – Comprehensive evaluation of patient’s current weight, satiety level, and eating patterns
- Establishment of weight loss targets – Setting realistic milestones for each adjustment phase
- Determination of adjustment intervals – Typically ranging from 4-8 weeks during active weight loss
- Adjustment volume calculation – Precise saline volume based on restriction requirements
Most patients require approximately 4-6 adjustments during the first year post-surgery. The frequency generally decreases in subsequent years, with maintenance adjustments occurring every 6-12 months. Research from bariatric centers indicates patients receiving properly timed adjustments achieve 15-20% greater excess weight loss compared to those with inadequate adjustment schedules.
The concept of progressive tightening has gained clinical support, where small incremental adjustments (0.25-0.5cc) produce better outcomes than larger, less frequent fills. This approach minimizes discomfort while maintaining the optimal restriction zone where patients experience appropriate hunger control without obstruction risks.
Recovery and Post-Adjustment Dietary Guidelines
Following a band adjustment, proper dietary management becomes crucial for optimal recovery and long-term success. Appropriate nutritional choices help minimize discomfort while maximizing the effectiveness of the adjusted restriction.
First 24 Hours After Adjustment
- Clear liquids only for the first 24 hours to allow swelling to subside and prevent blockage
- Sip slowly throughout the day, aiming for 64-80 ounces of sugar-free, non-carbonated fluids
- Avoid temperature extremes as very hot or cold liquids may cause discomfort
- Monitor for adequate hydration by checking urine color (should be light yellow to clear)
- Take prescribed medications as directed, crushing pills when possible or using liquid alternatives
- Rest adequately while maintaining gentle movement like short walks to aid digestion
First Week After Adjustment
- Progress gradually from liquids to pureed foods by day 2-3 if tolerating fluids well
- Introduce soft foods like yogurt, cottage cheese, and well-cooked vegetables by day 4-5
- Consume protein-rich options such as scrambled eggs, pureed chicken, or protein shakes
- Eat small portions of 2-3 tablespoons per meal, increasing gradually as tolerated
- Chew thoroughly until food reaches applesauce consistency before swallowing
- Wait 30 minutes between consuming solids and liquids to prevent overfilling
- Track food intake in a journal to identify any problematic foods causing discomfort
Long-term Nutrition Plans
- Prioritize protein consumption of 60-80 grams daily to preserve muscle mass during weight loss
- Include nutrient-dense foods like lean proteins, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
- Practice mindful eating techniques by eating slowly and stopping at the first sign of fullness
- Maintain vitamin supplementation as recommended by your healthcare provider
- Stay hydrated with water throughout the day, aiming for 64 ounces minimum
- Avoid problematic foods that commonly cause discomfort such as bread, pasta, and tough meats
- Schedule regular nutritional assessments with your dietitian to adjust your plan as needed
- Incorporate moderate exercise as approved by your healthcare team to maximize results
Signs That Your Gastric Band Needs Adjustment
Recognizing when your laparoscopic adjustable gastric band requires fine-tuning is crucial for maintaining weight loss progress and overall health. The following indicators suggest it may be time to consult your bariatric surgeon:
- Increased hunger that wasn’t present before, particularly if you’re consuming larger portions than your post-surgery recommended amounts
- Weight loss plateau or unexpected weight gain despite adhering to your prescribed dietary guidelines
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or food getting stuck when eating normal-textured foods
- Regurgitation or vomiting after meals, especially when this occurs regularly
- Nighttime coughing or acid reflux symptoms that disturb sleep patterns
- Excessive salivation during meals that wasn’t previously experienced
- Pain or discomfort in the upper abdominal region, particularly during or after eating
- Feeling full after only a few bites then experiencing hunger again shortly after meals
- Heartburn or GERD symptoms that have increased in frequency or severity
- Ability to consume foods that were previously difficult to eat following your initial band placement
The optimal band adjustment creates a feeling of controlled satiety without uncomfortable restriction. Research indicates that patients requiring proper band adjustments report a 15-20% improvement in quality of life scores following appropriate modifications. Many bariatric specialists note that responsive band management plays a significant role in achieving long-term excess weight loss targets of 40-60%.
Potential Complications of Gastric Band Adjustments
Gastric band adjustments, while generally safe, can lead to several potential complications that patients should be aware of. These issues range from mechanical problems with the band itself to physiological reactions that may require medical intervention.
Band Slippage
- Persistent upper abdominal pain that worsens after eating or drinking
- Increased heartburn or reflux symptoms not responding to medication
- Night coughing or aspiration of food, particularly when lying down
- Inability to keep food down even after small meals
- Radiographic evidence showing band displacement on X-ray studies
- Immediate medical attention required as this can lead to obstruction
Band Erosion
- Gradual reduction in weight loss effectiveness despite proper band tightness
- Port site infection that doesn’t resolve with antibiotics
- Unexplained fever or systemic inflammatory response
- Abdominal pain that differs from normal post-adjustment discomfort
- Blood in stool or vomit indicating potential erosion into the stomach wall
- Requires surgical intervention as the band may need to be removed
Port Problems
- Discomfort or pain around the port site that persists beyond normal healing
- Rotation of the port making it difficult or impossible to access for adjustments
- Leakage causing incomplete band filling or deflation between adjustments
- Visible tubing under the skin indicating port or tubing displacement
- Infection signs including redness, warmth, or drainage at port site
- Swelling or fluid collection around the port requiring drainage
Over-tightening Complications
- Difficulty swallowing even properly chewed food or liquids
- Persistent vomiting after consuming minimal amounts of food
- Nocturnal regurgitation causing sleep disruption or aspiration risk
- Dehydration symptoms including dizziness, headache, and dark urine
- Severe food intolerance leading to nutritional deficiencies
- Esophageal dilation which may be detected through imaging studies
- Requires prompt band loosening to prevent permanent esophageal damage
Long-term Success After Gastric Band Adjustments
Maintaining long-term success following gastric band adjustments requires consistent adherence to several key strategies. Sustainable weight management depends on both physical and psychological factors that work together to support your bariatric journey.
Successful maintenance strategies include:
- Regular follow-up monitoring with your bariatric team to assess weight trends and overall health markers
- Maintaining detailed food and activity journals to identify patterns and triggers
- Implementing mindful eating practices that focus on hunger and fullness cues
- Developing sustainable meal planning routines that prioritize protein and nutrient-dense foods
- Building strong support networks including both professional and personal connections
The long-term maintenance phase should incorporate a structured exercise regimen:
- Begin with a professional fitness assessment to establish appropriate baseline activities
- Gradually increase intensity as fitness levels improve
- Incorporate both cardiovascular and strength training elements
- Schedule regular fitness reassessments every 3-6 months
Psychological adaptation remains equally important for lasting success. Many patients benefit from ongoing support in this area:
- Participate in regular support group meetings with fellow bariatric patients
- Work with a psychologist specialized in weight management
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms for emotional challenges
- Set realistic expectations about weight maintenance patterns
The relationship between band adjustment optimization and long-term success is significant. Research indicates that patients who maintain regular contact with their bariatric team achieve 15-20% better maintenance of their weight loss over a 5-year period compared to those who discontinue follow-up care.
By integrating these comprehensive strategies into your lifestyle, you can maximize the effectiveness of your gastric band and enjoy sustainable weight management for years to come.