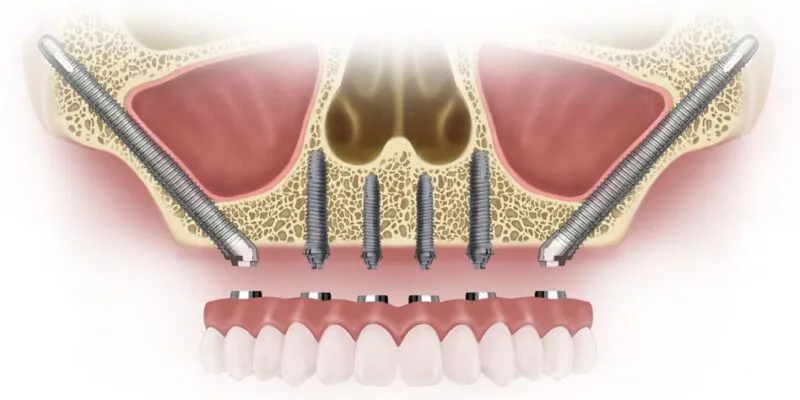
Severe maxillary bone loss presents significant reconstructive challenges for dental implant placement. Traditional approaches often necessitate extensive bone grafting procedures. These procedures are frequently associated with prolonged treatment times and increased patient morbidity. For instance, large-scale studies demonstrate graft failure rates ranging from 5% to 20%, depending on the complexity of the case. In such scenarios, conventional implant solutions may not be viable or predictable. Zygoma implants offer a well-established alternative for patients with pronounced atrophy. Their unique anchorage in the malar bone bypasses the need for grafting in many cases. This provides a fixed prosthesis solution where others fail, supported by decades of clinical success.
Table of Contents
How Do Zygomatic Implants Differ from Traditional Dental Solutions?
Zygomatic implants represent a fundamentally different approach to dental restoration compared to conventional implant systems. These specialised solutions address severe bone deficiency cases where traditional dental implants cannot achieve adequate stability.
The following comparison demonstrates the key distinctions between zygomatic or zygoma implants and standard dental restoration methods:
| Feature | Traditional Dental Implants | Zygomatic Implants |
|---|---|---|
| Placement location | Maxillary or mandibular bone | Zygomatic arch/cheekbone |
| Implant length | 8-16mm typically | 30-55mm extended length |
| Bone requirement | Adequate alveolar bone | Minimal alveolar bone needed |
| Angulation | Vertical placement | Angled through sinus cavity |
| Osseointegration site | Local jawbone | Zygoma bone implant area |
The primary distinction lies in anchoring methodology. Whilst conventional implants rely on sufficient alveolar bone density, zygomatic bone implants utilise the robust zygomatic arch as their foundation. This structural difference enables treatment for patients with significant maxillary bone loss who would otherwise require extensive bone grafting procedures.
Single-piece zygomatic implant designs offer enhanced stability through their monolithic construction. Unlike traditional two-piece systems, these implants eliminate the implant-abutment junction, reducing potential failure points and bacterial infiltration risks. The continuous structure extends from the zygomatic arch through the maxillary sinus to the oral cavity.
What are zygomatic implants in terms of surgical complexity? These procedures demand advanced surgical expertisedue to their proximity to vital anatomical structures. The placement trajectory passes through the maxillary sinus, requiring precise three-dimensional planning to avoid complications. Traditional implants follow straightforward vertical placement protocols with minimal anatomical considerations.
Recovery patterns differ substantially between these approaches. Zygoma implants dental procedures typically involve more extensive initial healing due to sinus involvement and soft tissue manipulation. However, immediate loading protocols often enable same-day prosthetic attachment, contrasting with traditional implants that may require several months of osseointegration before restoration.
The biomechanical advantages of zygomatic arch implants include superior load distribution characteristics. Their extended length and cortical bone engagement provide exceptional primary stability, often exceeding 35 Ncm insertion torque values. Traditional implants depend entirely on local bone quality, which may compromise stability in compromised sites.
Patient selection criteria represent another fundamental difference. Zygomatic implant vs normal dental implant candidacy assessment focuses on anatomical considerations rather than bone quantity alone. Suitable patients require adequate zygomatic bone density and appropriate sinus morphology, whilst traditional implants primarily assess local alveolar dimensions.
Prosthetic considerations also distinguish these treatment modalities. Zygoma implants typically support full-arch rehabilitations due to their strategic positioning and angulation. The emergence profile often requires customised abutment designs to accommodate the implant trajectory, whereas traditional implants offer standardised prosthetic components for various restoration types.
Long-term maintenance protocols vary between systems. Zygomatic implants require specialised radiographic monitoring to assess sinus health and implant integrity. Traditional implants follow conventional peri-implant tissue evaluation methods with standard radiographic techniques, making ongoing care more straightforward for general practitioners. This distinction can be as significant as the difference in Chin Implant Genioplasty Price, given that zygoma implants intersect with anatomical structures like the sinus. Proper monitoring and specialist consultation are vital components of ensuring successful outcomes with these complex implants.
Understanding the Zygomatic Implant Procedure: Step by Step
The zygomatic implant procedure represents a sophisticated surgical approach that enables patients with severe upper jaw bone loss to receive fixed dental restorations. This comprehensive surgical technique requires meticulous planning and precise execution to achieve optimal outcomes.
Pre-Operative Planning
The foundation of successful zygomatic implant surgery lies in thorough pre-operative assessment and planning. Our experience demonstrates that comprehensive evaluation significantly influences surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
- Three-dimensional imaging assessment using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) provides detailed anatomical visualization of the maxillary and zygomatic bone structures, enabling precise surgical planning
- Medical history evaluation focuses on systemic conditions, medications, and previous dental treatments that may influence healing and surgical success
- Anatomical analysis includes measurement of zygomatic bone density, sinus anatomy, and available bone volume to determine optimal implant positioning
- Prosthetic planning involves detailed assessment of occlusion, vertical dimension, and aesthetic requirements for the final restoration
- Risk assessment evaluation encompasses patient-specific factors such as smoking history, diabetes management, and oral hygiene capabilities
- Surgical guide preparation utilizes digital planning software to create precise templates that ensure accurate implant placement angles and positions
The planning phase typically requires 2-3 weeks to complete all necessary assessments and coordinate with the prosthetic team. Advanced imaging technology allows surgeons to virtually plan the entire zygomatic implant surgery before entering the operating theatre.
Surgical Technique and Step-by-Step Process
The zygomatic implant surgery follows a systematic approach that ensures predictable placement and immediate stability. This procedure requires advanced surgical expertise and specialized instrumentation.
- General anaesthesia administration ensures patient comfort throughout the procedure, with monitoring systems maintaining optimal physiological parameters during surgery
- Surgical site preparation involves thorough disinfection and sterile draping of the maxillofacial region, following strict aseptic protocols
- Mucoperiosteal flap elevation exposes the lateral maxillary wall and zygomatic buttress area through carefully planned incisions that preserve vital anatomical structures
- Pilot hole creation begins with precise drilling at the alveolar crest, following the predetermined trajectory towards the zygomatic bone body
- Sequential drilling protocol utilizes progressively larger drill sizes to prepare the osteotomy site while maintaining optimal bone preservation and cooling
- Implant insertion involves placement of the zygomatic implant through the maxillary sinus, engaging the dense zygomatic bone for primary stability
- Torque measurement confirms adequate primary stability, typically achieving 35-50 Ncm insertion torque for immediate loading protocols
- Soft tissue management includes careful suturing techniques that promote optimal healing and minimize post-operative complications
Each surgical step requires continuous irrigation to prevent thermal bone damage and maintain visibility throughout the procedure. The entire zygomatic implant procedure typically requires 2-4 hours depending on the number of implants placed and anatomical complexity.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Post-operative management plays a crucial role in ensuring successful osseointegration and long-term stability of zygomatic implants. Our clinical experience emphasizes the importance of structured recovery protocols.
- Immediate post-operative care includes ice application for the first 48 hours to minimize swelling and detailed pain management protocols using prescribed analgesics
- Antibiotic therapy typically involves 7-10 days of amoxicillin or alternative antibiotics for patients with allergies to prevent surgical site infections
- Dietary modifications require soft food consistency for the first 2-3 weeks, gradually progressing to normal texture as healing progresses
- Oral hygiene protocols emphasize gentle cleaning around surgical sites using prescribed antimicrobial rinses and soft-bristled toothbrushes
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled at 1 week, 2 weeks, 6 weeks, and 3 months to monitor healing progression and implant stability
- Prosthetic loading typically occurs within 24-72 hours for immediate loading protocols, or after 3-4 months for conventional loading approaches
- Long-term maintenance requires regular professional cleanings and radiographic monitoring to ensure continued implant health and stability
Patients experience varying degrees of facial swelling and discomfort during the first week following zygomatic implant surgery. Most individuals return to normal activities within 10-14 days, though complete soft tissue healing requires 4-6 weeks.
Investment and Pricing: How Much Do Zygomatic Implants Cost?
The financial investment for zygomatic implants represents a significant consideration for patients seeking advanced dental rehabilitation. These specialised titanium implants command premium pricing due to their complex design, surgical requirements, and exceptional outcomes for patients with severe bone loss.
The following table outlines comprehensive pricing structures for zygomatic implant treatments:
| Treatment Component | UK Cost Range | Turkey Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Single Zygomatic Implant | £3,500-£5,000 | £1,200-£2,000 |
| Nobel Zygoma Implants (pair) | £8,000-£12,000 | £2,500-£4,000 |
| Complete All-on-4 with Zygoma | £15,000-£25,000 | £5,000-£8,500 |
| Surgical Fees | £2,000-£4,000 | £800-£1,500 |
| Prosthetic Crown/Bridge | £1,500-£3,000 per unit | £400-£800 per unit |
| Total Treatment Package | £18,000-£35,000 | £6,000-£12,000 |
Several critical factors influence the total investment required for zygomatic implant procedures:
- Implant System Selection: Nobel zygoma implants typically command higher pricing due to their established clinical track record and advanced surface technology
- Surgical Complexity: Cases requiring bilateral zygomatic placement increase overall treatment costs significantly
- Geographic Location: Treatment costs vary substantially between countries, with Turkey offering 60-70% savings compared to UK pricing
- Clinic Reputation: Established maxillofacial surgery centres with extensive zygoma experience charge premium rates
- Additional Procedures: Bone grafting, sinus lifts, or extractions add £500-£2,000 per procedure
- Prosthetic Requirements: Fixed bridgework costs more than removable alternatives but provides superior function
Insurance coverage for zygomatic implants remains limited in most policies. NHS funding applies only to exceptional medical circumstances requiring maxillofacial reconstruction. Private insurance plans occasionally provide partial coverage for medically necessary cases.
Financial planning options include extended payment plans, medical loans, and treatment abroad programmes. Many UK patients combine Turkish treatment with brief recovery holidays, maximising cost savings while receiving quality care.
The substantial price difference between countries reflects varying operational costs rather than treatment quality. Turkish clinics utilise identical Nobel Biocare zygomatic systems and comparable surgical protocols to UK practices.
Zygomatic implants cost reflects their sophisticated engineering, surgical expertise requirements, and exceptional long-term success rates. While the initial investment appears substantial, these implants provide decades of reliable function, making them cost-effective solutions for complex dental rehabilitation cases requiring immediate loading capabilities.