Gum recession, a prevalent condition, manifests as the displacement of the gum margin from the crown of the tooth, exposing the root surface. This critical issue, often a consequence of periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, or genetic predisposition, necessitates advanced intervention to prevent further dental degradation. Dental grafting gum, also known as a gingival graft or gum graft, stands as a highly effective surgical procedure designed to restore lost gum tissue, protect exposed tooth roots, and enhance the overall health and aesthetics of the oral cavity. This authoritative guide delves into the intricacies of gum grafting surgery, offering a comprehensive overview for individuals considering this essential periodontal treatment.
Table of Contents
Receding gums not only compromise the structural integrity of the teeth by increasing sensitivity to hot and cold but also elevate the risk of root decay, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, such as a gum transplant, are paramount in mitigating these adverse effects. The objective of gum grafting is to cover exposed roots with healthy tissue, thereby reducing sensitivity, preventing further recession, and creating a more harmonious gum line.
Understanding Gum Recession and Its Implications
Gum recession is a progressive condition that, if left unaddressed, can lead to severe dental complications. It often signals underlying oral health issues that require professional attention. Recognizing the causes and consequences is the first step toward effective management.
Causes of Gum Recession
Several factors contribute to the development of receding gums:
- Periodontal Disease: This is the most common cause. Bacterial infections destroy gum tissue and the bone supporting the teeth, leading to gum detachment and recession.
- Aggressive Tooth Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can physically wear away gum tissue over time.
- Insufficient Dental Hygiene: A lack of proper brushing and flossing allows plaque to accumulate and harden into tartar, fostering bacterial growth and gum inflammation (gingivitis graft).
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are inherently more susceptible to gum disease and recession, irrespective of their oral hygiene habits.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly in women during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to recession.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and other forms of tobacco use significantly increase the risk of periodontal disease and contribute to gum recession.
- Misaligned Teeth or Bite Problems: When teeth do not come together properly, excessive force can be placed on certain areas, leading to gum tissue damage.
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding/Clenching): Chronic grinding or clenching can exert undue pressure on the gums and supporting bone, leading to recession.
- Piercings: Lip or tongue piercings can irritate gum tissue, leading to localized recession.
Consequences of Untreated Gum Recession
The implications of neglecting receding gums extend beyond cosmetic concerns:
- Increased Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed tooth roots lack the protective enamel layer, making them highly sensitive to temperature changes and certain foods.
- Root Decay: The cementum covering the tooth root is softer than enamel and more susceptible to decay, leading to cavities.
- Bone Loss: Severe gum recession is often accompanied by underlying bone loss, which can destabilize teeth.
- Tooth Mobility and Loss: As supporting structures diminish, teeth can become loose and eventually fall out.
- Compromised Aesthetics: A visibly uneven gum line and elongated teeth can impact self-confidence.
- Difficulty Cleaning: Exposed root surfaces can be harder to clean effectively, exacerbating plaque buildup and gum disease.
Types of Gum Grafting Procedures
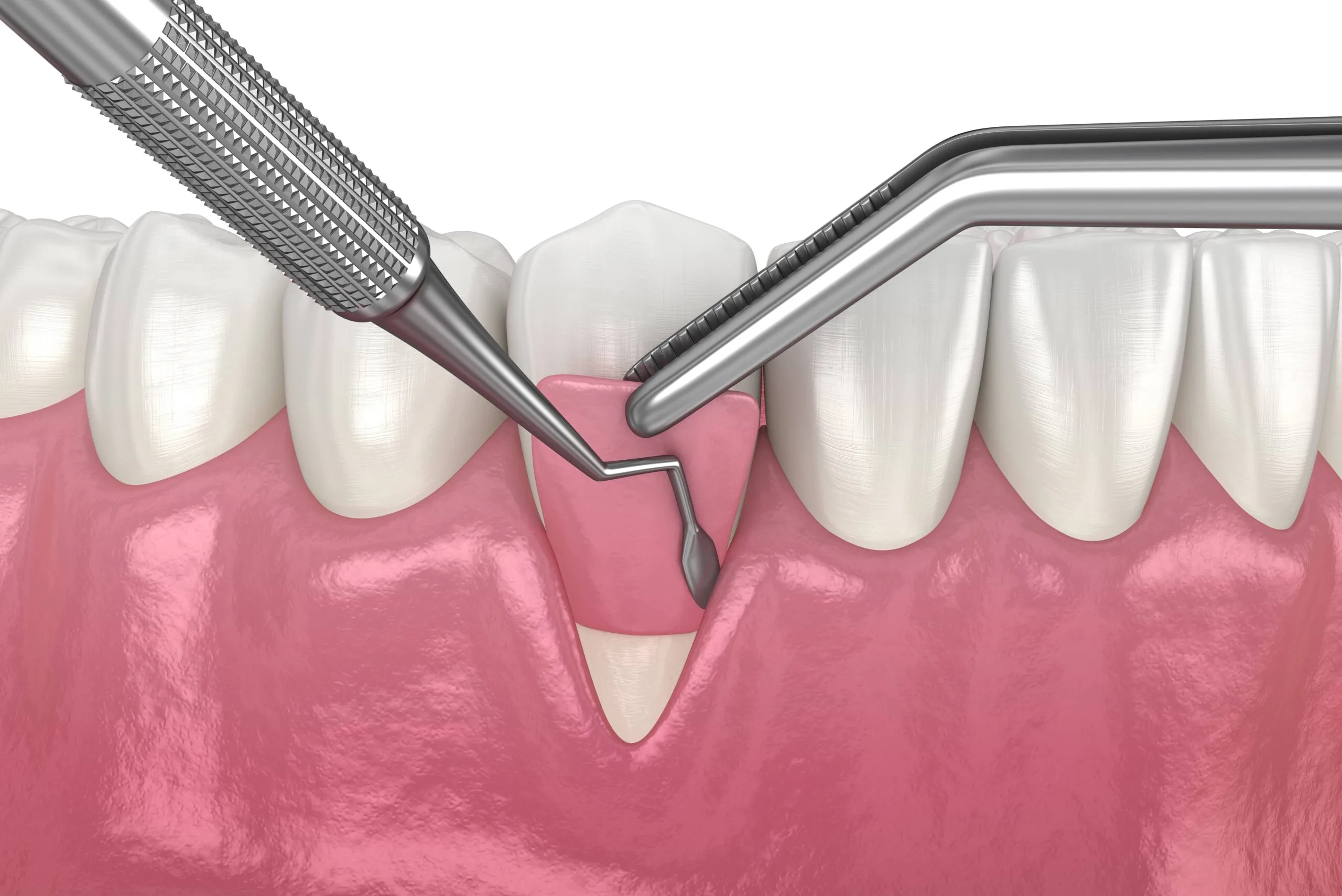
Gum grafting surgery involves taking healthy gum tissue from one area of the mouth (usually the palate) and attaching it to the receded area. Several techniques are employed, each suited for specific clinical situations. Understanding what is a gingival graft and its variations is crucial for an informed decision.
1. Connective Tissue Graft
This is the most common and effective method for treating root exposure. A small flap of skin is cut on the roof of the mouth, and tissue from underneath the flap (subepithelial connective tissue) is removed. This tissue is then stitched to the existing gum tissue around the exposed root. The flap on the palate is then repositioned and sutured. This technique provides excellent results for root coverage and a natural appearance.
2. Free Gingival Graft
Similar to a connective tissue graft, but a small piece of tissue is taken directly from the surface of the roof of the mouth and stitched to the area of recession. This method is often used to thicken thin gum tissue or to increase the amount of keratinized tissue around the teeth. While effective, it may not provide as natural an aesthetic outcome as the connective tissue graft due to the difference in tissue appearance.
3. Pedicle Graft (Lateral or Coronal Positioning)
This procedure involves creating a flap of gum tissue adjacent to the area of recession, which is then pulled over to cover the exposed root and stitched into place. This method is only feasible if there is sufficient gum tissue next to the receding area. A pedicle graft offers the advantage of maintaining blood supply to the grafted tissue, promoting faster healing. Variations include laterally positioned flaps (moved from the side) or coronally positioned flaps (moved upwards towards the crown).
The Gum Grafting Procedure: What to Expect
Undergoing a gum graft is a minor surgical procedure typically performed under local anesthesia. The process involves meticulous planning and execution to ensure optimal results.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
- Comprehensive Examination: The dentist or periodontist will conduct a thorough examination of your mouth, including X-rays, to assess the extent of gum recession and bone loss.
- Discussion of Options: All available grafting surgery gums options will be discussed, outlining the most suitable technique for your specific condition.
- Oral Hygiene Review: You will receive instructions on optimal oral hygiene practices to ensure your mouth is as clean as possible before the surgery.
- Medication Review: Inform your dentist about any medications you are taking, especially blood thinners, as adjustments may be necessary.
During the Procedure
On the day of the procedure, local anesthesia will be administered to numb the treatment area. The chosen grafting technique will then be performed with precision. The donor tissue, if required, will be harvested from the palate or an adjacent site. This tissue is then carefully placed over the exposed root surface and secured with sutures. A periodontal dressing may be applied to protect the surgical site.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
Adhering to post-operative instructions is critical for successful healing and integration of the gum implant. Patients can expect some discomfort, swelling, and minor bleeding after the procedure.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication will manage discomfort.
- Diet: For the first few days, consume soft foods and avoid chewing on the surgical site.
- Oral Hygiene: Gently brush remaining teeth, avoiding the surgical area. Your dentist may recommend a special antimicrobial mouthwash.
- Activity: Avoid strenuous physical activity for a few days to minimize bleeding and promote healing.
- Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing and remove sutures if necessary.
Long-Term Outcomes and Effectiveness
The long-term success of gingival graft procedures is well-documented. A systematic review and meta-analysis by Tavelli et al. (2019) on the long-term esthetic and clinical outcomes of gingival recession treatment highlighted the efficacy of various soft tissue grafting techniques, particularly connective tissue grafts, in achieving significant root coverage and improving esthetic parameters over extended periods. The study underscored the predictability and stability of these procedures, emphasizing their crucial role in managing gingival recession and enhancing overall periodontal health. This evidence reinforces the clinical importance of such interventions in preserving tooth structure and preventing further recession.
Proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are essential to maintain the results of the gum grafting surgery and prevent future recession. These procedures not only restore gum tissue but also significantly improve the prognosis for affected teeth, safeguarding against further damage and enhancing overall dental care in Turkey.
Comparing Gum Grafting in Turkey vs. the United Kingdom
Patients from the United Kingdom increasingly seek advanced dental treatments, including dental grafting gum, in international locations like Turkey. The decision often hinges on a balance of cost, quality, and accessibility. Turkey has emerged as a prominent destination for dental tourism, offering competitive pricing without compromising on medical standards.
Factors for Comparison
| Factor | Turkey | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|
| Cost-Effectiveness | Significantly lower, often 50-70% less | Higher, reflecting higher operational costs |
| Availability of Appointments | Shorter waiting times, greater flexibility | Potentially longer waiting lists, especially for specialist procedures |
| Clinic Standards & Technology | Many clinics boast state-of-the-art equipment and internationally trained staff | High standards, well-regulated, but can vary by practice |
| Travel & Accommodation | Requires international travel, often bundled with tourist packages | No international travel, local convenience |
| Post-Operative Care | Often includes follow-up scheduling, remote consultation options | Typically local follow-up, though travel may be required for specialists |
Price Comparison for Gum Grafting Procedures
For patients considering gum grafting, the financial aspect is often a significant determinant. The cost of dental procedures in Turkey is notably more accessible compared to the United Kingdom, making it an attractive option for those seeking high-quality care at a reduced price point.
| Service/Item | Turkey Price (GBP) | UK Price (GBP) |
|---|---|---|
| Single Site Gum Graft | £700 – £1200 | £1500 – £3000 |
| Multiple Sites Gum Graft | £1500 – £2500 | £3500 – £6000 |
| Connective Tissue Graft | £900 – £1500 | £1800 – £3500 |
| Alloderm Graft (Acellular Dermal Matrix) | £1000 – £1800 | £2000 – £4000 |
*Note: Prices are estimates and can vary based on the specific clinic, complexity of the case, and additional services.*
This significant cost difference enables patients to access premium care, often with the added benefit of combining their treatment with a travel experience. Furthermore, clinics in Turkey are often equipped with modern technology and staffed by highly qualified professionals, ensuring a standard of care comparable to or exceeding that found in many Western countries.
CK Health Turkey: Your Partner for Advanced Dental Solutions
At CK Health Turkey, we understand the critical importance of specialized dental care, including advanced procedures like dental grafting gum. We are committed to providing international patients, particularly those from the UK, with exceptional and comprehensive dental care Turkey. Our state-of-the-art facilities, combined with a team of highly experienced periodontists and dental surgeons, ensure that you receive the highest standard of treatment. From the initial consultation to post-operative follow-up, we prioritize patient comfort, safety, and optimal outcomes. Whether you require a single gum graft or complex full-mouth rehabilitation, CK Health Turkey offers tailored treatment plans designed to meet your individual needs. We also provide comprehensive support for patients seeking dental implants in Turkey, ensuring a holistic approach to your oral health. Contact us today to schedule your consultation and embark on your journey towards superior oral health and a confident smile.
FAQs
What is dental grafting gum and why is it necessary?
Dental grafting gum, also known as a gingival graft or gum graft, is a surgical procedure to restore gum tissue lost due to recession. It is necessary to protect exposed tooth roots from decay, reduce sensitivity, prevent further gum loss, and improve the aesthetic appearance of the gum line.
How long does the gum grafting procedure take?
The actual procedure for a single site gum graft typically takes 60-90 minutes. However, this can vary based on the number of sites being treated and the complexity of the case.
Is gum grafting painful?
The procedure itself is performed under local anesthesia, so you should not feel any pain. Post-operative discomfort, swelling, and minor bleeding are common, but these can be effectively managed with prescribed pain medication and adherence to post-operative care instructions.
What is the recovery time for a gum graft?
Initial healing usually takes 1-2 weeks. During this time, you should follow a soft diet and avoid strenuous activities. Complete healing and tissue integration can take several weeks to a few months, with regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress.
What are the different types of gum grafts?
The primary types include connective tissue grafts (most common for root coverage), free gingival grafts (to thicken thin gums), and pedicle grafts (using adjacent gum tissue, suitable for localized recession). The best type depends on your specific condition and needs.
Are there alternatives to gum grafting surgery?
For minor recession, your dentist might recommend improved oral hygiene techniques or restorative dental procedures like dental bonding to cover exposed roots. However, for significant recession and progressive gum disease, gum grafting surgery is often the most effective and durable solution.
How successful is gum grafting?
Gum grafting procedures have a high success rate, particularly connective tissue grafts, in achieving stable root coverage and improving periodontal health. Long-term success is largely dependent on maintaining excellent oral hygiene and attending regular dental check-ups.
Can gum recession return after a graft?
While successful gum grafts provide long-lasting results, recession can recur if the underlying causes (e.g., aggressive brushing, untreated periodontal disease) are not addressed. Consistent oral hygiene and regular dental visits are crucial for preventing recurrence.
Will my insurance cover gum grafting?
Coverage for gum grafting varies significantly among dental insurance plans. It is often considered a restorative procedure, which may be partially covered. It is advisable to check with your insurance provider for detailed information regarding your specific policy.
How do I choose the right periodontist for my gum graft?
When selecting a periodontist, look for a board-certified specialist with extensive experience in periodontal surgery and gum grafting. Consider their reputation, patient testimonials, and the technology available at their clinic. A thorough consultation should also clarify their approach and answer all your questions.