For severe Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), especially in obese patients, bariatric surgery for GERD offers a potent treatment. This guide explores its mechanisms, advantages, and implications, providing a thorough perspective for individuals considering this intervention, particularly within the United Kingdom context.
Table of Contents
Understanding GERD and Obesity
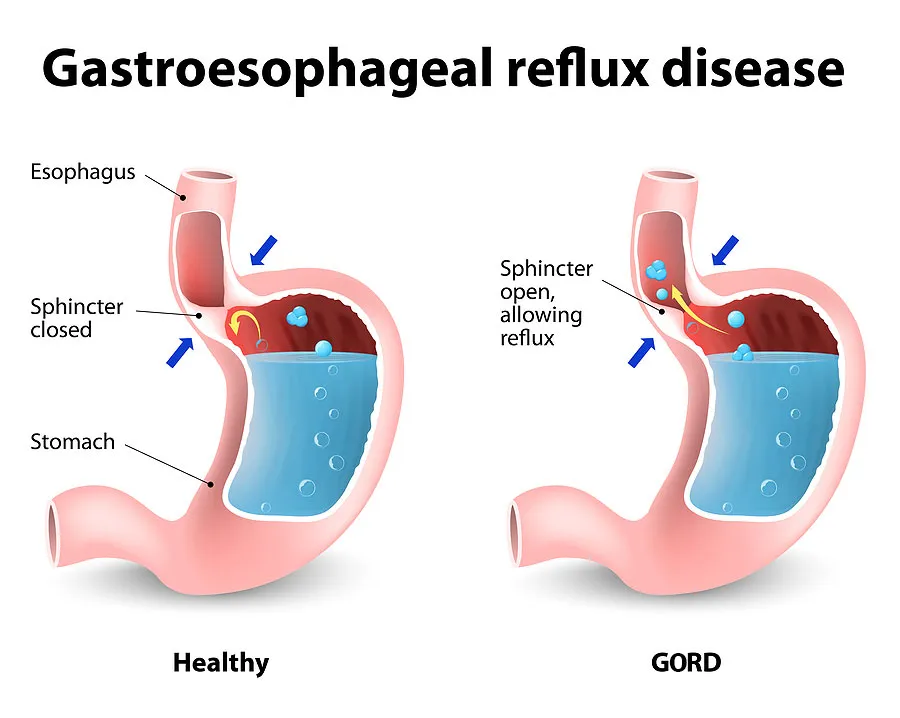
GERD manifests with symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, dysphagia, and chronic cough, significantly impacting quality of life. Its underlying cause is often a weakened lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), which acts as a valve between the oesophagus and the stomach. When this sphincter does not close properly, stomach contents can reflux. While various factors contribute to GERD, a strong correlation exists with obesity.
The Link Between Weight and Reflux
Excess body weight, particularly central obesity, increases intra-abdominal pressure. This elevated pressure can push stomach acid upwards against a weakened LES, exacerbating reflux symptoms. Adipose tissue also produces hormones and inflammatory mediators that may contribute to oesophageal dysfunction. For many individuals with obesity, weight loss is a critical component of GERD management. However, for those with severe obesity and refractory GERD, bariatric surgery not only facilitates substantial weight loss but also directly addresses anatomical and physiological factors contributing to reflux.
When Conservative Treatments Fail
Initial management of GERD typically involves lifestyle modifications (dietary changes, elevating the head of the bed, avoiding triggers) and pharmacological interventions, primarily proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). While effective for many, a subset of patients experiences persistent symptoms despite maximal medical therapy. This condition, known as refractory GERD, often prompts consideration of surgical options. For these patients, particularly when obesity is a comorbidity, surgical intervention may offer superior long-term outcomes and resolution of symptoms. The decision to pursue surgery is a significant one, requiring thorough evaluation and consideration of all available treatments.
Bariatric Surgery for GERD: A Definitive Solution
Bariatric surgery, primarily known for its efficacy in treating obesity, has demonstrated remarkable success in resolving or significantly improving GERD in many patients. The procedures work through various mechanisms, including weight loss, anatomical alterations that strengthen the anti-reflux barrier, and hormonal changes.
How Bariatric Procedures Address Reflux
Different bariatric procedures impact GERD in distinct ways. Gastric bypass, for instance, is highly effective due to its fundamental restructuring of the digestive tract. It creates a small gastric pouch and reroutes food directly to the jejunum, bypassing the majority of the stomach and the duodenum. This design reduces the volume of acid produced by the stomach and lessens the exposure of the oesophagus to acid. Additionally, the new anatomy can act as a more effective barrier against reflux. Other procedures, such as sleeve gastrectomy, also induce significant weight loss, which can indirectly alleviate GERD by reducing intra-abdominal pressure.
Gastric Bypass: The Gold Standard
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is widely considered the most effective bariatric procedure for resolving GERD, often leading to complete remission or significant improvement of symptoms. The mechanism involves several factors: creating a small gastric pouch significantly reduces acid-producing capacity, and diverting bile and pancreatic secretions away from the oesophagus reduces irritation. The new gastrojejunal anastomosis also creates a functional anti-reflux barrier. Research consistently demonstrates that RYGB effectively treats GERD in morbidly obese patients, leading to long-term symptom resolution and cessation of reflux medication.
Sleeve Gastrectomy and GERD
Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving a narrow, tube-like ‘sleeve.’ While highly effective for weight loss, its impact on GERD is more nuanced. For some patients, SG can improve GERD symptoms due to significant weight loss and reduced stomach volume. However, in others, it may potentially worsen or induce new GERD due to increased intra-gastric pressure and changes to the angle of His (the angle between the oesophagus and the stomach). A study published in the *Annals of Surgery* (2018) investigating the long-term impact of sleeve gastrectomy on GERD found that while many patients experienced improvement, a notable percentage developed new or worsened reflux symptoms post-operatively. The research highlighted that factors such as pre-existing GERD severity and the presence of a hiatal hernia can influence outcomes, underscoring the importance of careful patient selection and pre-operative evaluation when considering bariatric surgery for GERD in the context of sleeve gastrectomy. For patients with severe pre-existing GERD, gastric sleeve surgery may require careful consideration or an alternative procedure like gastric bypass.
Other Surgical Options
While RYGB and SG are the most common procedures, other bariatric surgeries also exist. For instance, Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS) is another highly effective option for both weight loss and GERD resolution, though it is a more complex procedure. This surgery involves a significant reduction in stomach size combined with intestinal rerouting, leading to profound weight loss and metabolic improvements, including excellent GERD resolution rates.
Eligibility Criteria and Pre-Surgical Evaluation
Undergoing bariatric surgery for GERD is a major decision requiring a thorough evaluation process to ensure patient suitability and optimal outcomes. Not every patient with GERD or obesity is a candidate for surgery.
Medical Assessment
Candidates for bariatric surgery are typically individuals with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with significant obesity-related comorbidities such as GERD, type 2 diabetes, or sleep apnoea. A comprehensive medical assessment includes evaluating cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and metabolic status. Diagnostic tests like upper endoscopy, oesophageal manometry, and pH studies are often performed to assess the severity of GERD, identify any oesophageal damage (e.g., Barrett’s oesophagus), and rule out other conditions. This rigorous evaluation ensures that the chosen surgical approach is safe and maximally effective for the patient’s specific circumstances.
Psychological Preparedness
Beyond physical health, psychological readiness is paramount. Patients must demonstrate a clear understanding of the surgical process, realistic expectations for outcomes, and a commitment to long-term lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular physical activity. Psychological evaluations help identify any contraindications such as untreated severe mental health conditions, substance abuse, or unrealistic expectations that could hinder post-operative success. Support systems and access to post-operative care are also crucial considerations.
The Surgical Process: What to Expect
Understanding the surgical journey, from preparation to immediate recovery, helps patients approach the procedure with confidence and clarity.
Pre-Operative Preparation
Preparation for bariatric surgery is intensive and typically begins weeks or even months before the scheduled date. This phase includes:
- Dietary Modifications: Patients are often required to follow a strict pre-operative diet, typically low-calorie and low-carbohydrate, to reduce liver size and body fat, making the surgery safer.
- Medical Clearances: Obtaining clearances from various specialists (e.g., cardiologist, pulmonologist, endocrinologist) to ensure all medical conditions are optimally managed.
- Smoking Cessation: Complete cessation of smoking is mandatory several weeks prior to surgery to minimize respiratory complications and improve healing.
- Medication Review: All medications are reviewed, and some may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued.
- Education: Extensive education is provided regarding the surgical procedure, potential risks, and post-operative dietary and lifestyle requirements.
The Procedure Itself
Most bariatric surgeries are performed laparoscopically, involving several small incisions rather than a large open incision. This minimally invasive approach results in less pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. The specific steps of the procedure, whether it’s a gastric bypass or another form of weight loss surgery, will be thoroughly explained by the surgical team. Patients are under general anaesthesia throughout the procedure, which typically lasts between 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Following surgery, patients are closely monitored in the hospital. Key aspects of immediate post-operative care include:
- Pain Management: Administering pain medication to ensure comfort.
- Fluid Intake: Starting with small sips of water and gradually progressing to a liquid diet.
- Mobility: Early ambulation (walking) is encouraged to prevent blood clots and promote recovery.
- Monitoring for Complications: Close observation for any signs of complications such as bleeding, infection, or leaks.
- Patient Education: Continued instruction on dietary progression and activity restrictions before discharge.
Recovery and Long-Term Outcomes
Recovery from bariatric surgery is a phased process, extending well beyond the initial hospital stay. Long-term success hinges on adherence to medical advice and lifestyle changes.
Initial Recovery Phase
The first few weeks post-surgery are critical. Patients typically spend 2-4 days in the hospital, followed by several weeks of recovery at home. During this time, physical activity is restricted, and a strict liquid diet transitions to pureed foods, then soft solids. Pain and discomfort are managed with medication, and fatigue is common as the body heals and adapts to new dietary patterns. Regular follow-up appointments with the surgical team and a dietitian are essential to monitor progress and address any concerns.
Dietary Adjustments and Lifestyle Changes
Successful long-term outcomes for bariatric surgery for GERD depend heavily on permanent lifestyle changes. Patients must commit to a high-protein, low-carbohydrate, low-fat diet, consuming small, frequent meals. Hydration is crucial, but liquids must be consumed between meals, not with them. Regular physical activity becomes a cornerstone of life post-surgery, aiding weight maintenance and overall health. Psychological support groups and counselling can be invaluable resources during this transformative period, helping patients navigate emotional and behavioural challenges.
Potential Complications and Management
While highly effective, bariatric surgery carries potential risks, including bleeding, infection, leaks from staple lines, blood clots, and nutritional deficiencies. Long-term issues can include gallstones, hernias, and in some cases, persistent reflux or strictures. Careful patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and comprehensive post-operative care minimise these risks. Patients are educated on warning signs and symptoms to seek immediate medical attention if needed. Nutritional deficiencies are managed through lifelong supplementation of vitamins and minerals. For instance, patients may experience gallbladder issues post-sleeve gastrectomy, necessitating further medical attention.
Cost Comparison: Bariatric Surgery in Turkey vs. the UK
Patients from the United Kingdom increasingly look to international options for bariatric surgery due to factors such as long waiting lists, limited availability on the NHS for certain criteria, and often prohibitive costs in the private sector. Turkey has emerged as a prominent destination for medical tourism, offering world-class care at a significantly lower price point.
| Service/Item | Turkey Price | UK Price |
|---|---|---|
| Gastric Sleeve | £3,500 – £5,000 | £8,000 – £12,000 |
| Gastric Bypass | £4,500 – £6,500 | £10,000 – £15,000 |
| Revision Bariatric Surgery | £5,500 – £8,000 | £12,000 – £18,000 |
| Anti-Reflux Surgery (non-bariatric) | £2,500 – £4,000 | £6,000 – £10,000 |
*Note: Prices are estimates and can vary based on the clinic, surgeon’s experience, specific patient needs, and package inclusions. These figures are provided for general comparison only.*
Why Choose CK Health Turkey for Your Treatment
CK Health Turkey stands as a premier choice for international patients seeking high-quality bariatric and metabolic surgery, including effective solutions for GERD. Our commitment to patient care, combined with state-of-the-art facilities and highly experienced surgeons, ensures that you receive exceptional treatment standards. We specialise in providing comprehensive packages that cater to the unique needs of patients travelling from the UK, encompassing pre-operative assessments, the surgical procedure, and dedicated post-operative support. Our team understands the complexities of weight loss surgery and its profound impact on conditions like GERD, offering personalised care plans designed for optimal health outcomes. With CK Health Turkey, you gain access to innovative surgical techniques and a supportive environment focused on your long-term well-being. We prioritise patient safety, clinical excellence, and transparent communication, making us a trusted partner in your health journey. To explore how bariatric surgery can resolve your GERD symptoms and to receive a personalised consultation, we invite you to get in touch with our patient coordination team or visit our website for more information on Weight Loss Surgery in Turkey.
FAQs
Can bariatric surgery cure GERD?
Gastric bypass surgery has a high success rate in resolving GERD symptoms, often leading to complete remission. Sleeve gastrectomy’s effect on GERD is more variable; it can improve or, in some cases, worsen reflux, necessitating careful patient selection.
What type of bariatric surgery is best for GERD?
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is generally considered the most effective bariatric procedure for treating GERD, particularly for patients with severe or refractory reflux.
Is bariatric surgery a common treatment for GERD in non-obese patients?
Bariatric surgery is primarily indicated for patients with obesity. For non-obese individuals with GERD, other surgical options, such as Nissen fundoplication, are typically considered before bariatric procedures.
What are the long-term benefits of bariatric surgery for GERD?
Long-term benefits include significant reduction or complete resolution of GERD symptoms, cessation of acid-suppressing medications, improved quality of life, and sustained weight loss.
How long is the recovery period after bariatric surgery for GERD?
Initial hospital stay is typically 2-4 days, with full recovery and return to normal activities usually within 4-6 weeks. However, adherence to dietary and lifestyle changes is lifelong.
Are there any dietary restrictions after bariatric surgery for GERD?
Yes, patients must follow a strict, phased diet, starting with liquids and progressing to pureed and soft foods, then solid foods in small portions. High-sugar, high-fat, and highly processed foods are generally discouraged.
What if my GERD symptoms persist after bariatric surgery?
While rare, if GERD symptoms persist after bariatric surgery, further investigation may be required. This could involve diagnostic tests to assess the cause and determine if revision surgery or other interventions are necessary.
How does bariatric surgery compare to traditional anti-reflux surgery?
Bariatric surgery offers the dual benefit of weight loss and GERD resolution in obese patients. Traditional anti-reflux surgeries like fundoplication specifically address the reflux mechanism but do not lead to significant weight loss.
Will I need to take medications for GERD after bariatric surgery?
Many patients find they no longer need GERD medications after bariatric surgery, especially after gastric bypass, due to the significant improvement or resolution of their symptoms.
What support is available for patients post-surgery?
Comprehensive post-operative support typically includes follow-up appointments with the surgical team, dietitians, and access to support groups and psychological counselling to assist with adjustment and long-term success.