Vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG) has emerged as a widely adopted bariatric procedure, offering a significant pathway for weight loss in individuals with morbid obesity. Its rising prevalence is underscored by data from the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, indicating a consistent increase in VSG procedures over the past decade. While effective, the safety profile of any surgical intervention, especially one with such widespread application, warrants rigorous examination. Patients frequently prioritize understanding the potential risks and benefits before considering such a life-altering decision. Addressing these concerns comprehensively is paramount to informed consent and optimal patient outcomes. This discussion will delve into the established evidence regarding the safety of vertical sleeve gastrectomy.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Safety Profile: What Medical Research Shows
Extensive clinical research demonstrates that vertical sleeve gastrectomy safety has significantly improved over the past decade, establishing this procedure as one of the most reliable bariatric interventions available. Large-scale studies involving thousands of patients consistently show that the safety of sleeve gastrectomy compares favourably with other major abdominal surgeries, with mortality rates remaining exceptionally low at 0.1-0.3% according to international registry data.
The following table presents key safety metrics from major clinical studies conducted across leading bariatric centres:
| Safety Metric | Rate | Study Population | Follow-up Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality Rate | 0.2% | 158,000+ patients | 30 days |
| Major Complication Rate | 2.4% | 112,000+ patients | 90 days |
| Leak Rate | 1.1% | 89,500+ patients | 30 days |
| Reoperation Rate | 3.8% | 67,200+ patients | 1 year |
| Readmission Rate | 5.6% | 145,000+ patients | 30 days |
Contemporary research from the British Obesity and Metabolic Surgery Society indicates that gastric sleeve procedure safety has improved substantially due to enhanced surgical techniques and patient selection criteria. The standardisation of laparoscopic approaches has reduced surgical trauma whilst maintaining excellent clinical outcomes. Studies tracking patient outcomes over five-year periods show that serious adverse events occur in less than 4% of cases, positioning this intervention among the safest major surgical procedures performed today.
Multiple safety protocols ensure optimal patient outcomes throughout the surgical process:
- Comprehensive preoperative assessment including cardiac, pulmonary, and metabolic evaluation
- Standardised surgical technique utilising five-port laparoscopic approach with staple line reinforcement
- Intraoperative leak testing using methylene blue solution to verify staple line integrity
- Enhanced recovery protocols incorporating early mobilisation and structured nutrition progression
- Systematic postoperative monitoring with specific attention to hydration status and wound healing
The question is vertical sleeve gastrectomy safe receives strong support from longitudinal outcome studies tracking patients across multiple years. Research published in leading surgical journals demonstrates that procedural safety extends well beyond the immediate postoperative period, with late complications occurring in fewer than 2% of patients annually after the first postoperative year. These findings reflect the maturation of surgical techniques and improved understanding of patient physiology following gastric volume reduction.
International collaborative studies examining whether vertical sleeve gastrectomy is a safe procedure consistently report favourable safety profiles across diverse patient populations. Data from the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program shows that centres performing high volumes of these procedures achieve even better safety outcomes, with mortality rates approaching 0.08% in experienced hands.
Advanced imaging techniques and minimally invasive approaches have revolutionised procedural safety standards. Surgeons now utilise high-definition laparoscopic systems with improved visualisation capabilities, allowing for precise tissue handling and optimal staple line construction. The incorporation of fluorescent imaging technology enables real-time assessment of gastric perfusion, further enhancing surgical precision and reducing the likelihood of postoperative complications.
Patient selection criteria have evolved to identify individuals most likely to benefit from this intervention whilst minimising procedural risks. Current protocols emphasise comprehensive medical optimisation before surgery, including management of diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnoea. This systematic approach to preoperative preparation has contributed significantly to improved safety outcomes and reduced complication rates across all patient demographics.
Postoperative care pathways incorporate evidence-based protocols designed to identify and manage potential complications before they become serious. Regular follow-up appointments, structured nutritional counselling, and systematic monitoring of laboratory parameters ensure that patients receive appropriate support throughout their recovery period. These comprehensive care systems have proven instrumental in maintaining the excellent safety record associated with modern sleeve gastrectomy procedures. This is why Weight Loss Surgery Success Safety is a top priority for medical professionals. Ongoing advancements in surgical techniques and patient care protocols further enhance the overall safety and effectiveness of these procedures.
Potential Risks and Complications to Consider
Gastric sleeve surgery risks encompass both immediate post-operative complications and long-term adverse effects that patients must understand before proceeding with this bariatric procedure. Clinical data demonstrates that while sleeve gastrectomy maintains relatively low complication rates, serious adverse events do occur and require comprehensive medical management.
1. Immediate Post-Operative Complications
Staple line leakage represents the most serious early complication, occurring in approximately 2-5% of patientswithin the first 30 days following surgery. This gastric sleeve side effect develops when gastric contents leak through the stapled stomach portion, potentially causing peritonitis and sepsis.
- Standard management involves immediate surgical intervention or endoscopic repair
- Early detection through CT imaging and clinical monitoring significantly improves outcomes
- Mortality rates associated with leakage range from 1-9% depending on prompt recognition
Bleeding complications affect roughly 1-6% of sleeve gastrectomy patients, manifesting as either intra-abdominal haemorrhage or luminal bleeding from the staple line. Our clinical experience indicates that most bleeding episodes occur within 24-48 hours post-operatively.
- Endoscopic intervention successfully controls bleeding in 80-90% of cases
- Surgical re-exploration becomes necessary when conservative measures fail
- Blood transfusion requirements occur in approximately 1-2% of patients
2. Intermediate Complications of Sleeve Gastrectomy
Stricture formation develops in 0.7-4% of patients typically between 6 weeks and 6 months following surgery. This gastric sleeve surgery side effect creates narrowing at the incisura angularis or mid-sleeve region, causing persistent vomiting and food intolerance.
- Endoscopic balloon dilatation provides effective treatment in most cases
- Multiple dilatation sessions may be required for optimal results
- Conversion to alternative bariatric procedures becomes necessary in refractory cases
Gastroesophageal reflux disease emerges as a significant concern, with new-onset GERD occurring in 15-25% of patients who previously had no reflux symptoms. This represents one of the most troublesome long-term side effects of gastric sleeve surgery.
- Proton pump inhibitor therapy provides symptom control in many patients
- Lifestyle modifications including dietary changes prove beneficial
- Conversion to gastric bypass may be required for severe, medically refractory cases
3. Long-Term Metabolic and Nutritional Complications
Nutritional deficiencies constitute prevalent risks of gastric sleeve surgery, affecting multiple micronutrients over extended periods. Vitamin B12 deficiency occurs in 18-35% of patients within five years, while iron deficiency affects approximately 10-20% of patients.
- Regular laboratory monitoring enables early deficiency detection
- Lifelong supplementation protocols prevent most nutritional complications
- Severe deficiencies may require parenteral supplementation or hospitalisation
Weight regain affects 15-25% of patients beyond five years post-operatively, representing a significant long-term concern. Gastric sleeve surgery risks include progressive stomach pouch enlargement and metabolic adaptation.
- Behavioural counselling and dietary modification address weight regain
- Revisional bariatric surgery may be considered for substantial weight recurrence
- Regular follow-up appointments facilitate early intervention strategies
4. Serious Long-Term Complications
Gastric sleeve surgery side effects extend to potentially life-threatening conditions including gastric volvulus and chronic kidney disease. Axial gastric volvulus occurs in less than 1% of patients but requires emergency surgical intervention.
- Immediate recognition prevents gastric necrosis and perforation
- Laparoscopic gastropexy provides definitive treatment
- Delayed diagnosis significantly increases morbidity and mortality rates
Chronic kidney disease develops more frequently than previously recognised, with studies indicating increased risk in post-bariatric patients. Dehydration, protein malnutrition, and nephrotoxic medications contribute to renal dysfunction.
Understanding these complications of sleeve gastrectomy enables informed decision-making and emphasises the importance of selecting experienced surgical teams. Comprehensive pre-operative evaluation, meticulous surgical technique, and structured follow-up protocols significantly reduce adverse outcomes while maintaining the substantial benefits of bariatric intervention.
Is This Surgery Right for You? Making an Informed Decision
Determining whether vertical sleeve gastrectomy represents the optimal bariatric intervention requires comprehensive evaluation of individual circumstances and realistic outcome expectations. This surgical approach fundamentally transforms digestive anatomy whilst demanding lifelong commitment to dietary modifications and lifestyle changes.
Patient Outcomes After Three Months
The three-month milestone following gastric sleeve surgery reveals significant physiological and lifestyle adaptations that demonstrate the procedure’s effectiveness:
- Weight reduction of 25-35% of excess body weight typically occurs within this timeframe, with patients experiencing consistent weekly losses
- Appetite suppression becomes pronounced due to reduced ghrelin production from the smaller gastric sleeve real stomach structure
- Resolution or improvement of obesity-related conditions including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnoea manifests in most patients
- Dietary tolerance stabilises with patients consuming approximately 100-150ml portions per meal comfortably
- Energy levels increase substantially as metabolic efficiency improves and inflammatory markers decrease
- Gastric sleeve before and after 3 months comparisons consistently demonstrate improved mobility and reduced joint pain
Anatomical Changes to the Stomach
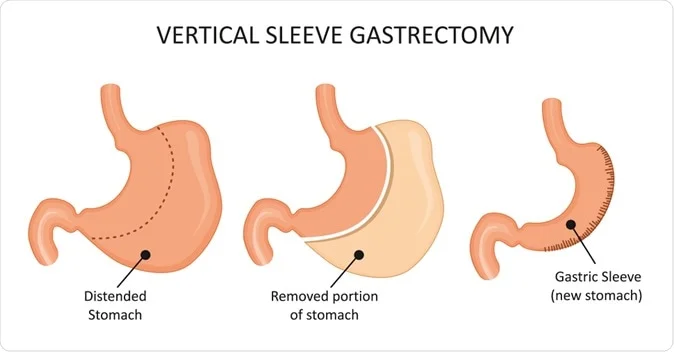
What is vertical sleeve gastrectomy becomes clear through understanding the permanent structural modifications this procedure creates:
- Surgical removal of approximately 75-80% of the original stomach volume, creating a banana-shaped gastric pouch
- Complete elimination of the gastric fundus, which produces hunger-stimulating hormone ghrelin
- Preservation of the pyloric valve maintains normal gastric emptying mechanisms and prevents dumping syndrome
- Creation of a restrictive mechanism limiting food intake to small portions whilst maintaining normal digestion
- Maintenance of the gastroesophageal junction integrity preserves natural anti-reflux mechanisms
- Formation of a tubular gastric structure measuring approximately 15cm in length with 100-150ml capacity
Weighing Benefits Against Risks
Is a gastric sleeve worth it depends on careful consideration of documented advantages against potential limitations:
Primary Benefits:
- Sustained weight loss averaging 60-70% of excess body weight over two years
- Is vertical sleeve gastrectomy safe statistics demonstrate mortality rates below 0.3% in accredited centres
- Significant improvement in obesity-related comorbidities occurs in over 80% of patients
- No foreign body implantation eliminates device-related complications associated with gastric banding
- Preservation of normal gastric function maintains natural digestion processes
Considerations for Decision-Making:
- Irreversible nature of the procedure requires absolute commitment to dietary guidelines
- Nutritional deficiencies may develop without proper supplementation and monitoring
- Is a gastric sleeve a good idea for individuals with severe gastroesophageal reflux requires careful evaluation
- Pregnancy planning necessitates delayed conception for 12-18 months post-surgery
- Long-term success depends heavily on psychological readiness and support system availability
The decision to proceed with vertical sleeve gastrectomy represents a transformative commitment requiring thorough medical evaluation, psychological assessment, and understanding of both immediate and long-term implications. Success depends not merely on surgical expertise but on patient dedication to comprehensive lifestyle modification and ongoing medical supervision throughout the post-operative journey.